A. Match the formal phrases on the left with the informal phrases on the right.
|
1 I deposited some money. 2 I withdrew some money. 3 The funds have been transferred. 4 My account is overdrawn. 5 It’s paid by standing order. 6 My account was debited. 7 My account was credited. 8 I used an ATM. 9 I made a balance enquiry. |
a. The money’s been sent. b. I paid in some money. c. It goes out of my account every month. d. I went to a cashpoint. e. I took out some money. f. I’m in the red. g. I checked my balance. h. It went into my account. i. It went out of my account. |
B. Match the words with the parts of the cheque.
account number amount in figures amount in words cheque number
logo payee signature sort code
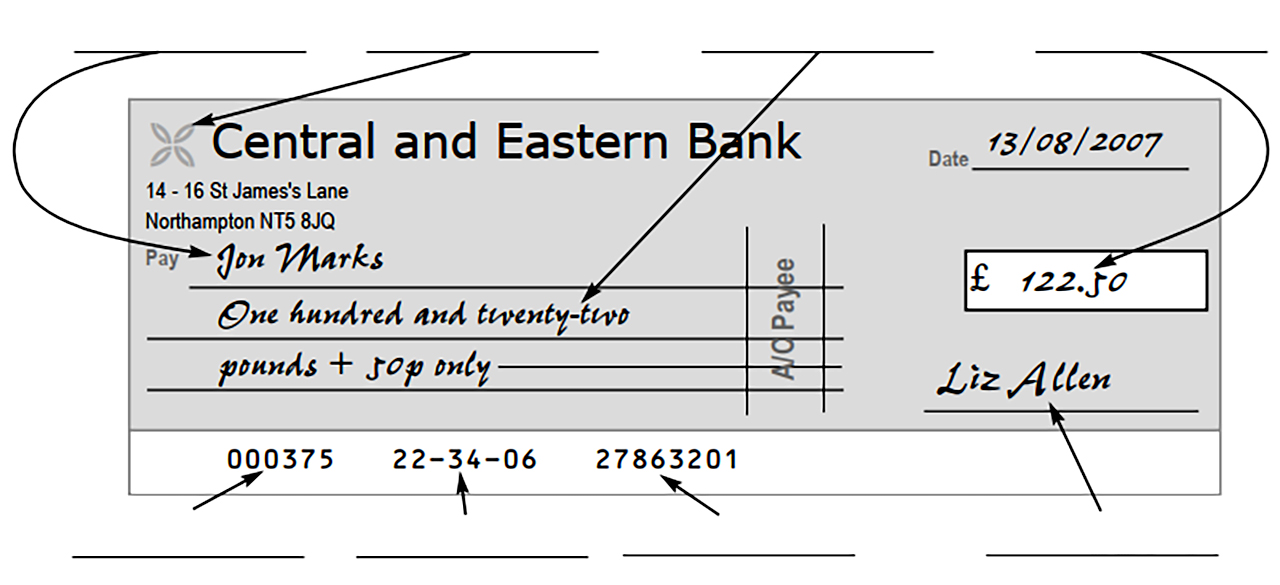
C. Answer the questions.
1 Who has this cheque been made out to? …………………………..
2 Has it been signed and dated? …………………………..
3 Is it crossed or uncrossed? …………………………..
4 Can it be paid into somebody else’s account? …………………………..
D. Choose the words to complete the sentences.
1 After they have been paid in, cheques usually take three working days to ………………………
a pass
b credit
c clear
2 When I write out a cheque, I keep a record by filling in the ………………………
a receipt
b invoice
c counterfoil
3 If you don’t have a cheque book, you can pay by getting a ……………………… from a branch of your bank.
a banker’s draft
b bank paper
c bank ticket
4 Unlike a personal cheque, a banker’s draft can’t ………………………
a be rejected
b bounce
c crash
5 A banker’s draft is also known as a bank draft or a ………………………
a banker’s cheque
b banker’s note
c banker’s ticket
6 If you need to borrow money, you can apply to your bank for an ………………………
a overdraft possibility
b overdraft facility
c overdraft opportunity
7 If you need to borrow more money from your bank, you can ask them to increase your ………………………
a overdraft limit
b overdraft level
c overdraft supply
8 If you want to borrow money from a third party*, you may have to supply a ………………………
a banker’s support
b banker’s promise
c banker’s reference
9 A banker’s reference proves to a third party that you are ………………………
a moneyed
b creditworthy
c rich enough
10 Regular automatic payments of the same amount (e.g. to a charity) are called ………………………
a standing orders
b direct debits
c direct orders
11 Regular automatic payments of varying amounts (e.g. electricity bills) are called ………………………
a standing orders
b direct debits
c direct orders
12 With my savings account, I have to ……………………… 30 days notice if I want to ……………………… a withdrawal.
a say / do
b give / make
c ask for / take
13 Many employees receive their salaries directly into their accounts by ………………………
a BACS payment
b BATS payment
c BAPS payment
14 BACS stands for Bankers Automated ………………………
a cheque system
b cost system
c clearing system
* “A third party” means another person or company
Answers
A: 1 b, 2 e, 3 a, 4 f, 5 c, 6 i, 7 h, 8 d (also known as a cash dispenser, cash machine and “hole-in-the-wall”), 9 g
B (from left to right): payee, logo, amount in words, amount in figures;
cheque number, sort code, account number, signature
C: Jon Marks, Yes, Crossed, No (because it’s been crossed)
D: 1 c, 2 c, 3 a, 4 b, 5 a, 6 b, 7 a, 8 c, 9 b, 10 a, 11 b, 12 b, 13 a, 14 c
